Spherical Geometry Operations
Pyresample provides some basic support for various geometrical calculations applicable to a spherical earth. These spherical operations are available for geometry definition objects. This includes for instance finding the intersection of two great circles or finding the area of a spherical polygon given by a set of great circle arcs.
The spherical geometry operations are calculated based on the corners of a GeometryDefinition
(GridDefinition,
AreaDefinition, or a 2D
SwathDefinition) assuming the edges are great circle arcs.
Geometries can be checked for overlap:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from pyresample.geometry import AreaDefinition
>>> from pyresample.geometry import SwathDefinition
>>> area_id = 'ease_sh'
>>> description = 'Antarctic EASE grid'
>>> proj_id = 'ease_sh'
>>> projection = '+proj=laea +lat_0=-90 +lon_0=0 +a=6371228.0 +units=m'
>>> width = 425
>>> height = 425
>>> area_extent = (-5326849.0625,-5326849.0625,5326849.0625,5326849.0625)
>>> area_def = AreaDefinition(area_id, description, proj_id, projection,
... width, height, area_extent)
>>> lons = np.array([[-40, -11.1], [9.5, 19.4], [65.5, 47.5], [90.3, 72.3]])
>>> lats = np.array([[-70.1, -58.3], [-78.8, -63.4], [-73, -57.6], [-59.5, -50]])
>>> swath_def = SwathDefinition(lons, lats)
>>> print(swath_def.overlaps(area_def))
True
The fraction of overlap can be calculated
>>> overlap_fraction = swath_def.overlap_rate(area_def)
>>> overlap_fraction = round(overlap_fraction, 10)
>>> print(overlap_fraction)
0.0584395313
And the polygon defining the (great circle) boundaries over the overlapping area can be calculated
>>> overlap_polygon = swath_def.intersection(area_def)
>>> print(overlap_polygon)
[(-40.0, -70.1), (-11.1, -58.3), (72.3, -50.0), (90.3, -59.5)]
It can be tested if a (lon, lat) point is inside a GeometryDefinition
>>> print((0, -90) in area_def)
True
Satellite swath coverage over area of interest
With this support and the help of Cartopy it is for instance also possible to draw the outline of a satellite swath on the earth, and calculate the relative coverage by one or more swaths over an area of interest.
Below is an example calculating how much of an area of interest is covered by
two satellite overpasses. It operates on a list of trollsched.satpass.Pass
satellite passes. See trollschedule how to generate a list of satellite overpasses.
area_def is an AreaDefinition object.
>>> from pyresample.spherical_utils import GetNonOverlapUnions
>>> from pyresample.boundary import AreaDefBoundary
>>> area_boundary = AreaDefBoundary(area_def, frequency=100)
>>> area_boundary = area_boundary.contour_poly
>>> list_of_polygons = []
>>> for mypass in passes:
>>> list_of_polygons.append(mypass.boundary.contour_poly)
>>> non_overlaps = GetNonOverlapUnions(list_of_polygons)
>>> non_overlaps.merge()
>>> polygons = non_overlaps.get_polygons()
>>> coverage = 0
>>> for polygon in polygons:
>>> isect = polygon.intersection(area_boundary)
>>> if isect:
>>> coverage = coverage + isect.area()
>>> area_cov = coverage / area_boundary.area()
>>> print("Area coverage = {0}".format(area_cov))
0.889317815
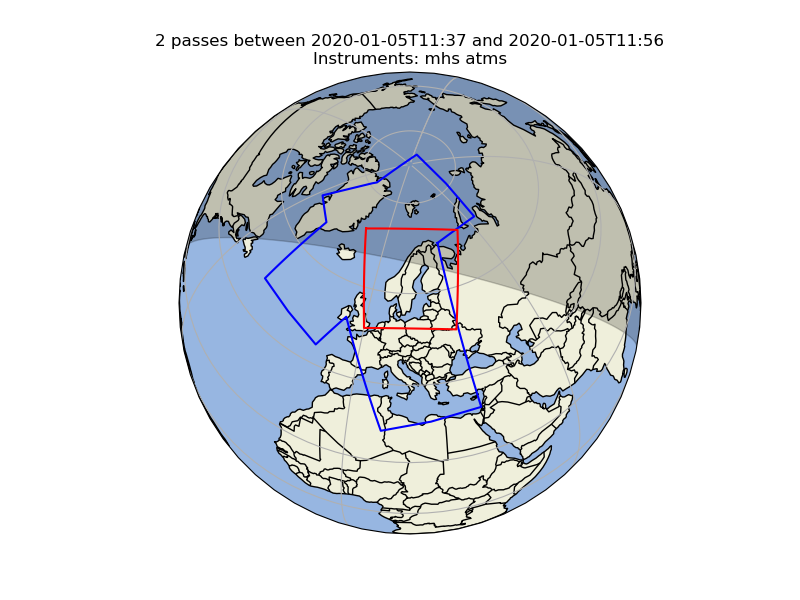
In this case the relative area covered by the two passes (blue outlines) over the area of interest (red outlines) is 89%.